Protein Only Helps In Muscle Development Myth Or Fact? Expert Reveals
Explore the truth about protein's role in muscle development as an expert reveals whether it's a myth or a fact. Gain valuable insights into optimizing your fitness journey.
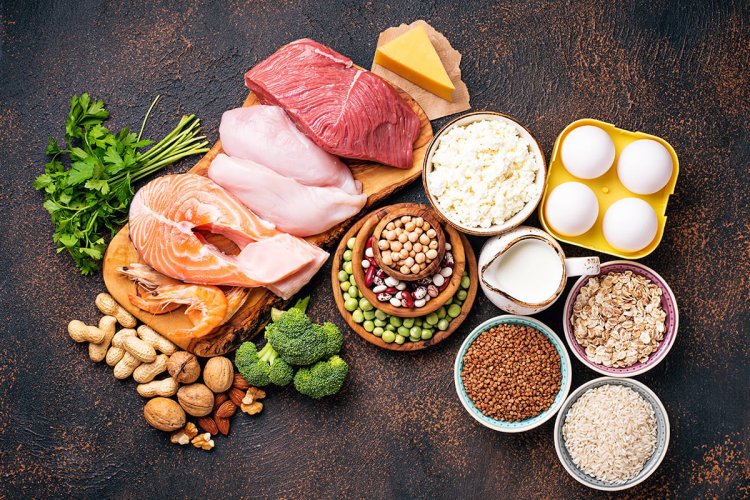

Along with muscles, skin, hair, and nails, protein is a crucial part of cellular structures, hormones, and antibodies. Since it's difficult to determine how much fat and carbohydrates to consume, protein has become the most widely consumed macronutrient. However, this does not mean that the protein cannot be misinterpreted. Most of us are aware that protein is only beneficial for building muscle. It is broken down by our bodies into amino acids, which are then used to rebuild and repair muscles.
That is only partly accurate, though, as protein serves purposes other than muscle growth. One of the three main food groups is protein, which is made up of amino acids that act as the "building blocks" for cells. For these cells to grow and heal, they require protein. You may get more protein in your diet from a few natural sources. Protein-rich foods that we can include in our regular diets include fish, poultry, eggs, lentils, and dairy products.How does protein support the growth of muscles?Muscle gain comes from protein. This vital element is necessary for all daily activities and bodily functions.
It's important to balance your total protein intake with the rest of your dietary intake, regardless of prevailing beliefs and presumptions about the appropriate amount of protein to ingest. Since the building elements of muscle tissue in your body are amino acids and protein, many people mistakenly associate protein with muscle mass. If the bricks that make up your muscles are called proteins.
Many of these amino acids are produced by your body, but only nine of them are known to be essential amino acids (EAAs) because the body is unable to produce them. Rather, you must get your EAAs from foods like soy, beans, and nuts. The creation of muscle proteins can be maximized with a diet rich in a variety of amino acids.
Leucine, an amino acid, is involved in numerous anabolic (muscle-building) activities. Because leucine in the right proportions triggers the production of muscle proteins, this is known as the "leucine trigger principle." Because amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins, aid in the maintenance and rebuilding of muscle tissue, protein is especially crucial for muscle growth. Protein aids in the healing process following an exercise session since activity causes little tears in the muscles.
Here are some intriguing suggestions for high-protein snacks that you can try
1. Peanut butter and rice cakes
The peanut butter will keep you full and supply protein, while the rice cake will provide you with energy.
2. Banana with yogurt
Greek yogurt is strained, which results in a higher protein content than regular yogurt. Before you do your pre-workout, try this food.
3. Any egg-based item
Not just for breakfast, eggs are a terrific food to eat at any time of the day. All of the essential amino acids your body needs to receive through the food are in them.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/__opt__aboutcom__coeus__resources__content_migration__serious_eats__seriouseats.com__images__2017__10__20171009-egg-breakfast-recipes-roundup-02-0d06fb82dd8a4b1f89fdd7f562fbcb80.jpg)
High-Protein Diet The Greatest Protein Sources, Both Vegetarian and Non-Vegetarian Additional vital nutrients that you need to consume in order to create muscle:You need to make sure you have the right ratio of nutrients and enough calories to last through your workout in order to build muscle mass effectively. The following are some additional nutrients that are important for muscular growth
1. Sugars and carbs
Many bodybuilders mistakenly view carbohydrates as competitors. Yes, sugars and highly processed carbohydrates are rarely helpful for the body. However, the proper kind of carbs, which are present in healthy grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables, support muscular function and mobility.
2. Fat
Athletes frequently undervalue dietary fat. Similar to carbohydrates, lipids may have an unjustified negative reputation. The correct fats in little amounts are crucial. Every type of cell membrane, including the membranes of muscle cells, depends structurally on fatty acids. The body uses fat as a fuel source for prolonged, low-intensity exercise.
3. Choline
It influences muscles by regulating their contractions. The regulation of heartbeats is involved, as the heart is a muscle that pumps blood. When the muscle activates the nerve, calcium is generated. In summary, it is utterly false. Not only is protein great for building muscle, but it also supports healthy hormone levels, the immune system, the brain, and hair. In summary, dietary protein promotes a robust immune system, aids in tissue growth and repair, and aids in the development of antibodies. In addition to protein, several additional nutrients such as calcium, zinc, vitamin D, carbohydrates, fats, and potassium are also necessary for the formation of muscle.